The GPU is a much more powerful processor as it breaks down the most complex calculations and finds solutions through the process of parallel processing. Because of the need to go through a lot of data while doing calculations, the GPUs have a faster and more advanced memory interface in comparison with a CPU.
GPU TYPES
There are different types of GPU available to users today and users can select the GPU that they want, depending on the purpose of work.
Integrated vs Discrete graphics
Single vs Multi GPU
GPU Market Breakdown
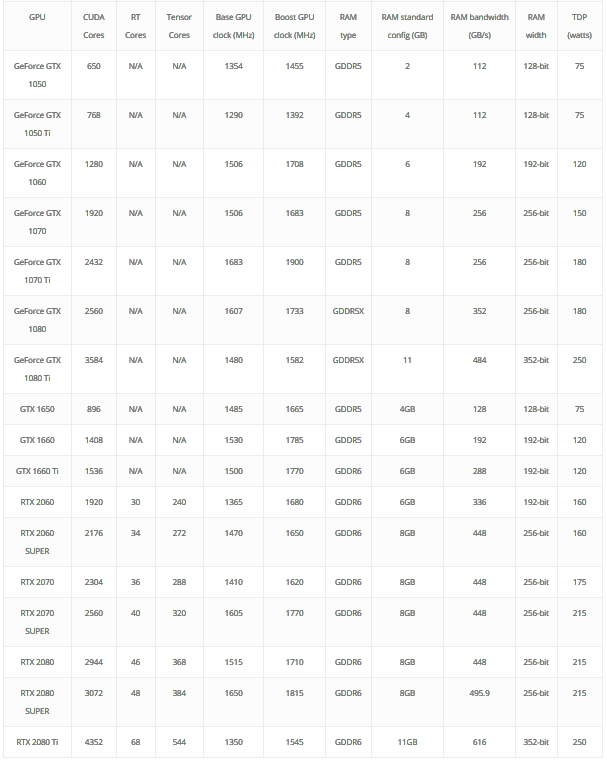
GPU Comparisons: NVIDIA AMD
NVIDIA and AMD are compatible with any processors. To have a well design system, make sure that the processor is powerful enough to keep up with the GPU you are selecting
Stream Processor/Cores
NVIDIA
AMD

Price Evaluations
TOP 3 Comparision
Feasibility Option
Choosing a GPU is based on which applications you are want to run as an engineer. NVIDIA and AMD are the two main owner of the GPU Market but they offer different performance based on different tech specifications. Looking at the Compatibility of the GPU matters especially the power supply that you want to use with the GPU that you are selecting. For selecting the power supply you will want know the input voltage and the conectors that interfaces the graphic card.
If you are choosing a GPU, NVIDIA is the best bet due to the fact that they own majority of the GPU market and a larger community of users. Meaning that it would be easier for users to get the help and support that they need if integration goes wrong. The reason NVIDIA are leaders of the GPU market for a reason as they put more resources into their software resources especially the CUDA libraries. They are versitile in ranges of memory, cost efficiency, price performance, deep learning, and image processing. AMD has a power GPU but based on many different user eperiences, they don't provide much support. NVIDIA is a safer choice.
At Nvidia, the GPU design is typically made of four categories which is the control circuitry, processing engines, display engines, and misc engines. The control circuitry includes a PMC (master control area), PBUS (bus control and an area where registers operates, PPMI (PCI Memory Interface that handles SYSRAM accesses from other units of the GPU), PTIMER (measures wall time and delivers alarm interrupts), PCLOCK+PCONTROL (clock generation and distribution), PFB (memory controller and arbiter, PROM (VBIOS ROM access), and PSTRAPS (configuration strap access). The processing engines includes PFIFO (gathers processing commands from the command buffers prepared by the host and delivers them to PGRAPH and PVPE engines in an orderly manner), PGRAPH (memory copying 2d and 3d rendering engine), PVPE (a trio of video decoding/encoding engines), and PCOUNTER (performance monitoring counters for the processing engines memory controller). The display engines consist of the PCRTC (generates display control signals and read framebuffer data for display), PVIDEO (reads and preprocesses overlay video data), PRAMDAC (multiplexes PCRTC, PVIDEO and cursor image data, applies palette LUT, converts to output signals) and PTV (an on-chip TV encoder). The misc engines has the PMEDIA (controls video capture input and mediaport, acts as a DMA controller.